News
Worried About Statin Side Effects? Discover How Policosanol Supports Heart Health Naturally
natural cholesterol support policosanol policosanol supplement
Heart health is a top concern for millions of adults worldwide, especially as they age or face increased risks due to diet, stress, or family history. Statins—commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol—are often the first solution people turn to. However, while effective, these medications can come with a laundry list of side effects that make some question whether the benefits outweigh the discomfort. Muscle pain, liver concerns, and digestive issues are just a few of the problems people report when taking statins.
If you're among those who worry about statin side effects or simply prefer a more natural approach, you're not alone. Thankfully, there's a plant-based alternative that’s gaining traction in the world of cardiovascular health: policosanol. Derived from sugarcane and other natural sources, policosanol has shown promising potential in supporting healthy cholesterol levels without the side effects commonly associated with statins. This article explores how policosanol works, why it’s considered a gentler alternative, and how it might be the heart-healthy addition your wellness routine needs.
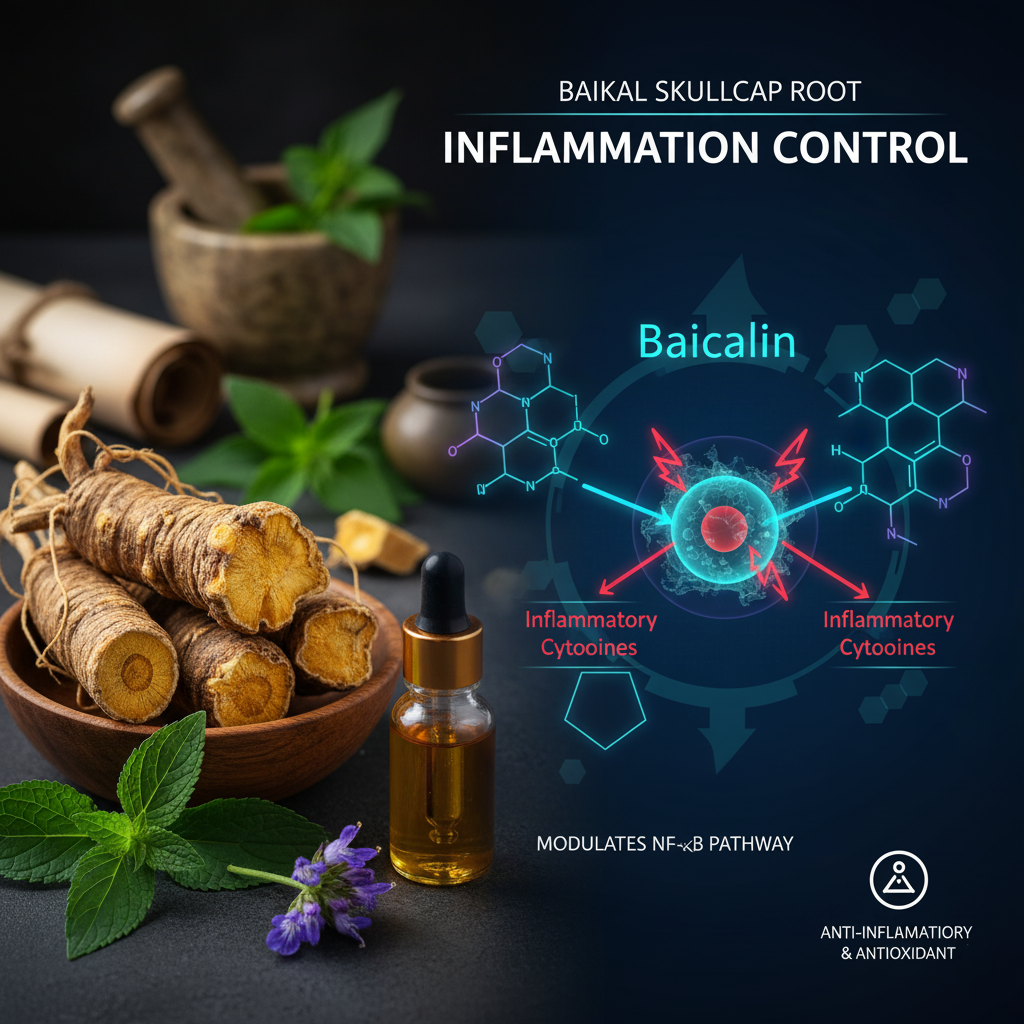
Harnessing Baicalin and Wogonin: How Baikal Skullcap Reduces Inflammation
baicalin and wogonin baikal skullcap benefits natural anti-inflammatory herbs
Chronic inflammation has become one of the most widespread health challenges of modern life, playing a central role in conditions ranging from joint pain to cardiovascular disease. But instead of turning solely to synthetic anti-inflammatories, a growing number of people are turning to nature’s pharmacopoeia—and one of its most promising stars is Baikal Skullcap.
This traditional Chinese herb contains two powerhouse flavonoids—baicalin and wogonin—that have caught the attention of scientists for their potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties. When paired with modern bioactive compounds like Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), the synergistic effects can amplify relief and support for those struggling with inflammation-related conditions. Let’s explore how Baikal Skullcap works, the science behind its compounds, and how to integrate it safely and effectively into your wellness routine.
The Science of Tart Cherry Juice: A Natural Melatonin Boost for Shift Workers
natural melatonin source shift worker sleep solutions tart cherry juice for sleep
Shift work can take a serious toll on your sleep-wake cycle, mood, cognitive performance, and overall health. When your circadian rhythm is disrupted, your body struggles to produce melatonin at the right times—leading to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue. For the millions of workers navigating night shifts, early morning shifts, or rotating schedules, finding a natural way to support restful sleep is essential.
Enter tart cherry juice—a vibrant, tangy beverage that’s gaining scientific attention for its natural melatonin content and sleep-enhancing effects. But that’s not all. Combining tart cherry juice with nootropic adaptogens like Bacopa Monnieri may offer shift workers a powerful one-two punch: deeper sleep and sharper daytime cognition. In this guide, we explore the evidence behind tart cherry juice for sleep, how it works with your body’s clock, and how to maximize its benefits for night owls and early risers alike.
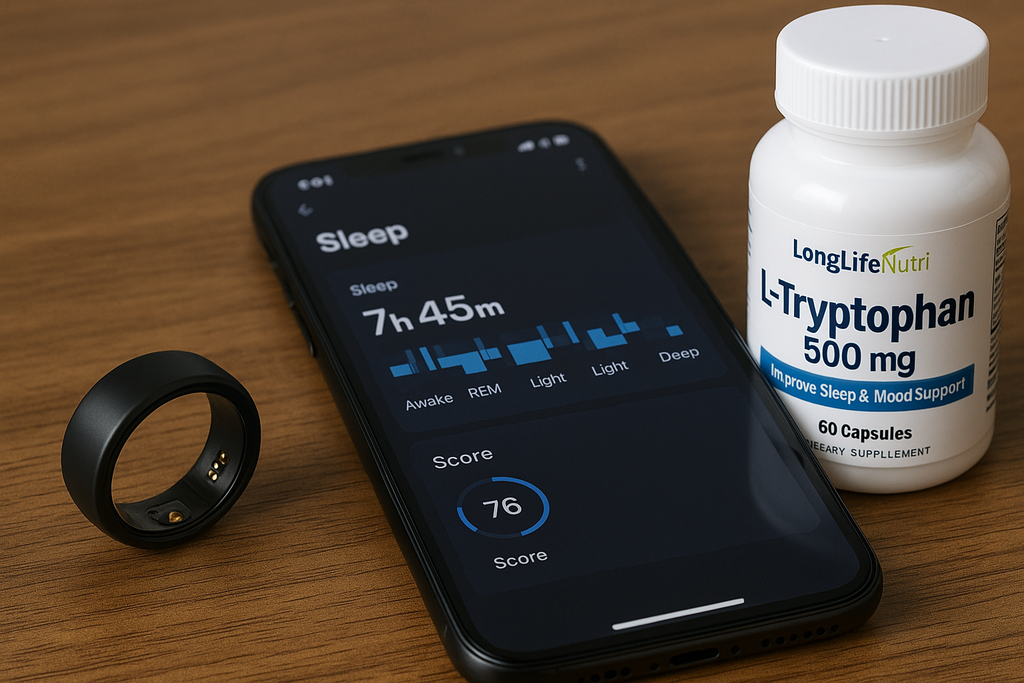
From Data to Deep Sleep: How to Use Your Smart Ring to Perfect Your Bedtime
how to use smart ring for sleep sleep optimization smart ring sleep tracking
In a world where technology has infiltrated every aspect of our daily routines, it's no surprise that sleep tracking has become a booming industry. Smart rings — those tiny, unobtrusive bands of biometric brilliance — are changing how we approach bedtime. From analyzing heart rate variability to detecting disruptions in REM cycles, these devices are more than just trendy gadgets; they’re insightful sleep coaches wrapped around your finger.
But understanding your smart ring's data is just the beginning. The real power lies in transforming that data into actionable changes that improve your sleep quality. That’s where the magic happens — combining technology with habits, supplements, and routines that support deep, restorative rest. Ready to learn how to turn numbers into nights of blissful slumber? Let’s dive into the science, strategy, and simplicity behind perfecting your bedtime routine with your smart ring.
The Antioxidant-Rich Sweetener: An Evidence-Based Guide to Sorghum Syrup
antioxidant-rich sweeteners natural sugar alternatives sorghum syrup benefits
In the quest for healthier alternatives to refined sugar, nature offers some surprisingly nutritious options. One such gem is sorghum syrup—a dark, rich, and flavorful sweetener derived from the juice of sorghum cane. Unlike conventional sweeteners, sorghum syrup is packed with antioxidants, essential minerals, and slow-digesting carbohydrates, making it not only a tasty addition to your pantry but also a functional ingredient in your wellness routine.
Often overshadowed by honey and maple syrup, sorghum syrup deserves the spotlight. It boasts a unique nutritional profile and plays a powerful role in oxidative stress reduction and chronic disease prevention. In this guide, we’ll explore the science-backed benefits of sorghum syrup, how it compares to other natural sweeteners, and how you can pair it with antioxidant-rich superfoods like Maqui Berry to amplify its effects.